Patents
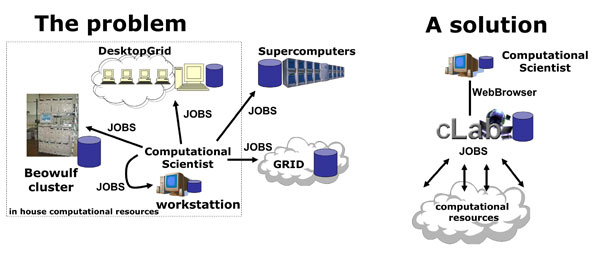
cLab: a web portal to access, use and manage computational resources
The Computational Laboratory Web Manager (cLab) is a web portal that permits the access and the management of a computational laboratory, which is a high performance hypercomputation center based on heterogeneous clusters of computers and used by multiple users simultaneously for the execution of computational jobs. cLab is an internet based application that allows users to manipulate files and folders, prepare computational tasks, submit and control them while they are running, as well as visualize or store results. cLab therefore provide tools for the users as well as for the system administrator.
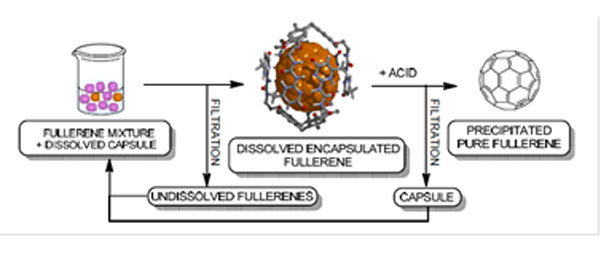
Purification of fullerenes by selective encapsulation mediated solid‐liquid extraction.
A concave compound self assembles thanks to reversible and controllable hydrogen bonding to form a dynamic capsule able to selectively extract fullerene derivatives of given size and shape. The process for the separation of fullerene derivatives is based on a sequential selective encapsulation in an appropriate solvent system of the fullerenes contained in a mixture. The capsule is formed by reversible self‐assembly of two concave fragments. The encapsulation of the fullerene derivative having the best fitting geometry for the cavity of the capsule is fast and selective.
• Fast and simple purification process (requires only 2 filtrations)
• Capsule is recyclable • Fullerenes and their derivatives are high value chemicals
• No specific equipment required
• Economically and environmentally sustainable process
• Capsule opening is dynamic and easily controlled (fast controllable extraction)
• Possibility to purify functionalized fullerenes from unfunctionalized ones
• Possibility to purify endofullerenes
USA (US-2014-0235866)
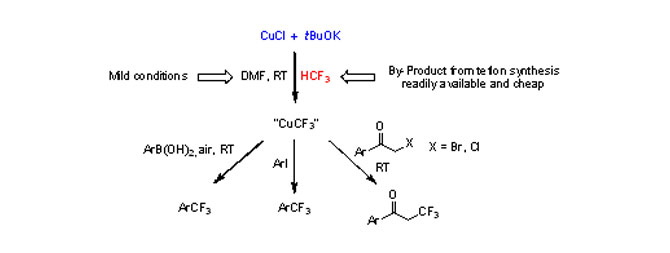
Process to obtain a trifluoromethylating composition
A process for the direct cupration of fluoroform has been developed. This exceedingly simple process employs only cheap reagents and is advantageously run at room temperature to produce CuCF3 reagents that are useful in trifluoromethylation reactions. Chemical compounds bearing a trifluoromethyl group are widely used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals as well as specialty materials, polymers, composites, building blocks, and intermediates for various needs. Fluoroform, CF3H, is an ideal source of CF3 because it is inexpensive, readily available in large industrial quantities, non‐toxic, and not an ozone depleter.
- clean production of trifluoromethyl reagents
- process works at room temperature and atmospheric pressure
- valorization of fluoroform (industrial waste)
- inexpensive and abundant trifluoromethyl source
- low‐cost reagents
The technology is currently the object of a R&D collaboration between ICIQ and a global company of the crop protection sector, with the aim of finding new synthetic applications of industrial relevance for the developed trifluoromethylating agent.
USA (US14401312)
China (CN104321293)
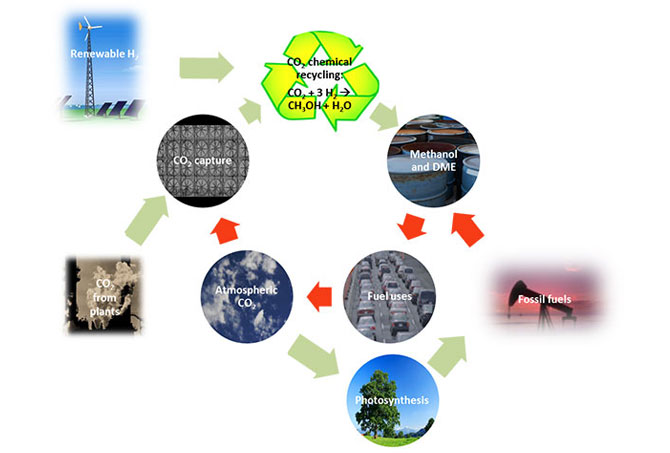
Process for the preparation of methanol and methanol-derived products from carbon oxides.
Chemical reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol and its derivatives (such as DME) is considered one of the key technologies to reduce both global warming and fossil fuels dependency. Unlike the currently used process for methanol synthesis, ICIQ’s process provides excellent conversions and selectivity to methanol in one pass through the reactor, thereby providing the highest time yield observed for the chemical reduction of CO2.
- High per-pass conversion
- High selectivity to methanol
- Use of conventional/commercial catalysts
- From CO2 to DME in one sole reactor
- Small reactor size
This technology has been the object of negotiations around a technology transfer agreement with a US-based energy company operating in China.
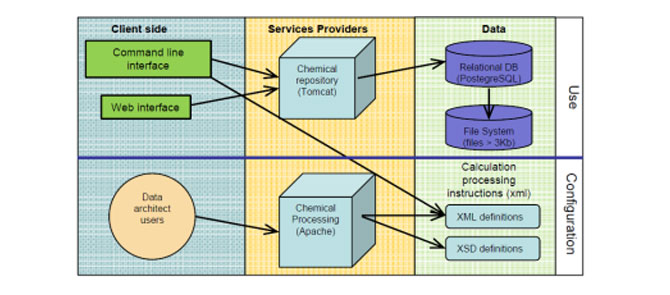
SCIPIO: a comprehensive software interface for computational chemists
SCIPIO is a software that allows to handle, store and manipulate output files from computational chemistry experiments. SCIPIO is a general data extractor and manager that is here presented as a Computational Chemistry Results Repository, which is a sort of tailored electronic notebook allowing for substructure searches and for the generation of “ready to publish” reports.
- Web and Command Line (bash) interface.
- Visualization of chemical structures
- General search & Substructure search
- Automatic generation of “Supporting Information” PDF files for direct publication.
- Calculation and Plotting of “Reaction Energy Profiles” by combining multiple results.
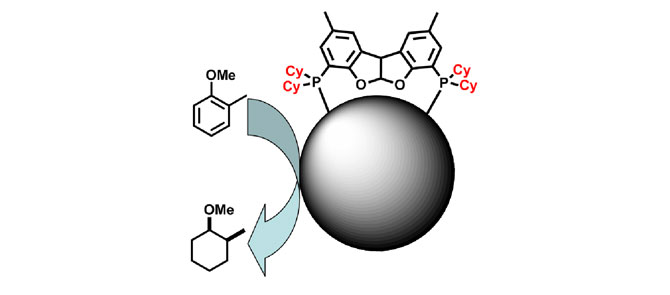
A compound comprising ruthenium nanoparticles supported on a solid support for the hydrogenation of aromatic compounds
A highly active and stable heterogeneous catalyst consisting in ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized with phosphine ligands embedded into a solid support has been developed. Hydrogenation of aromatics can be operated under mild conditions and under solvent free conditions, thereby rendering the process more sustainable and easy to implement. The catalyst can also be recycled at least 10 times without significant loss of activity, which makes it attractive for continuous flow applications.
- heterogenous catalyst
- catalyst is stable under air and easily recycled
- record activity in hydrogenation of aromatics
- catalyst operates in solvent-free conditions
- low amounts of catalyst required
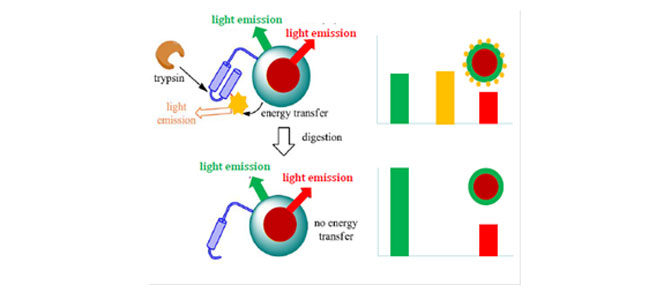
Ratiometric assay for the quantification of hydrolytic enzymes
A nanoparticle containing two different populations of chromophores and funcionalized with a dye-labelled peptide sensitive to the action of a hydrolytic enzyme has been developed. In that way, the optical response of the system can directly be correlated, in a quantitative manner, to the activity of a specific enzyme found in the medium where the nanoparticle is placed, thereby allowing for enzyme quantification. This technology was applied to cystic fibrosis, through the analysis of the trypsin amount of faeces samples. It was shown that this system could allow for the determination of patient’s phenotype, thus avoiding genetic testing.
- non-invasive diagnostic method
- accurate quantification of enzymatic activity
- method can be applied at point-of-care
- fast sample analysis
- Patient phenotype towards cystic fibrosis can be assessed
- Diagnostic platform is versatile
This technology has been further developed within a project of clinical validation of the diagnosis method funded by Fundació La Caixa and a ERC-Proof of Concept grant.
Bis-salphen compounds and carbon-based composite materials comprising them.
Gerhard Maier
A family of compounds able to form a network of rings interconnected by rods at the micro/nanoscopic scale through a self-assembly process has been developed. These compounds could successfully be incorporated into plastic materials in which the characteristic assembly is conserved. Within a polymer matrix containing carbon materials such as carbon nanotubes (composite material), the carbon particles aggregate around the self-assembled network, forming a network of dispersed and interconnected carbon materials, giving rise to e.g. lower percolation thresholds.
- Ease of implementation
- Compatible with organic solvents
- Improved properties of obtained material
- High processability of obtained materials (thermoplastic processes)
- Spontaneous dispersion of carbon nanotubes within the polymer matrix
This technology was developed through a partnership with the German company Polymaterials AG. A TECNIOSPRING grant (ACC1Ó) was granted for the development of commercial applications of the technology within a collaboration between ICIQ and Polymaterials AG, with a clear focus on market-driven research and technology transfer.
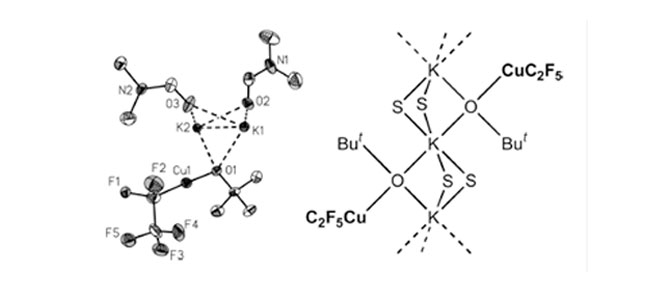
Pentafluoroethylating compositions
A process for the direct cupration of pentafluoroethane has been developed. This exceedingly simple process employs only cheap reagents and is advantageously run at room temperature to produce CuC2F5 reagents that are useful in pentafluoroethylation reactions. Chemical compounds bearing a pentafluoroethyl group are widely used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals as well as specialty materials, polymers, composites, building blocks, and intermediates for various needs. Pentafluoroethane, C2F5H, is an ideal source of C2F5 because it is inexpensive, readily available in large industrial quantities and non‐toxic.
- Clean production of pentaflyuoroethylation reagents
- Process operates in mild conditions (room temperature and atmospheric pressure)
- Valorization of pentafluoroethane (commonly used as a refrigerant)
- Abundant and cheap source of C2F5
- cheap reagents
Polymer supported phosphoric acis and use thereof in the preparation of 3-indolylmethanamines
3-indolylmethanamines, and more particularly their chiral derivatives, constitute a relevant family of compounds for the crop protection and pharmaceutical industries. The invention provides a polymer-supported organocatalysts that is highly active and selective for the preparation of such compounds by Friedel-Crafts reactions. Being supported on a polystyrene resin, the catalyst is easily recyclable by filtration and can be used under continuous flow conditions, making it suitable for process intensification and the preparation of libraries of chiral compounds.
- air stable and metal free catalyst
- active, selective and recyclable catalyst
- catalyst is suitable for continuous flow applications (process intensification and/or preparation of libraries of compounds)
This technology will be further developed within a valorization project funded by Fundació La Caixa.
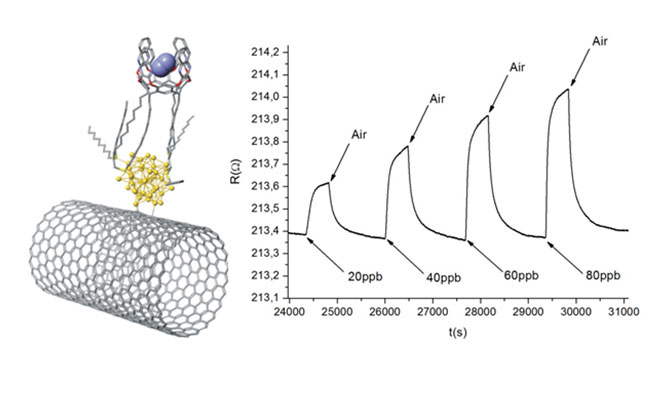
Resistive benzene gas sensor for air monitoring applications
Benzene is a highly toxic chemical, potentially carcinogen, for which it is necessary to control the exposure of workers and individuals to benzene, especially in industrial environments. The regulatory exposure limit of benzene is of 0.1 ppm during 8 hours or 1 ppm during 15 minutes. Therefore, it is important and necessary to dispose of quick, reliable and precise devices for the monitoring of said exposition of workers to benzene. A new device and process allowing for selectively detecting trace amounts of benzene with high sensitivity and in continuous mode, using cheap materials has been developed. The electrochemical sensor is based on a selective molecular receptor of benzene self-assembled onto gold nanoparticles attached to carbon nanotubes forming an electrode.
- Low cost. The technology allows developing a low cost sensor to detect the presence of benzene.
- High sensitivity. The lower limit of benzene detection for this technology is in the order of ppt (parts per trillion).
- High selectivity. Technology is highly selective for benzene.
- This technology does not require the use of consumables for detecting benzene.
- The technology allows the realization of continuous measurements. Some detectors on the market do not offer this possibility (PID technology).
The technology has been jointly developed by URV and ICIQ. Conditions for the joint ownership of the patent have been negotiated and funds for prototyping activities were obtained.
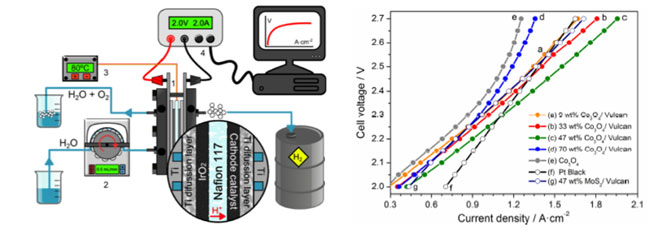
Cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen generation in PEM electrolyzers
PEM electrolysis of water is regarded as a promising solution for hydrogen production from renewable energies (e.g. wind and solar) and water. New materials are required to enhance the performance of such devices while diminishing its operation costs. The invention provides a catalyst based on carbon black and cobalt oxide nanoparticles, acting as a hydrogen evolution electrode with productivity similar or higher than platinum-based electrodes. This catalyst could substitute platinum in PEM cells.
- Heterogeneous catalyst based on cheap and abundant materials.
- Production of hydrogen comparable to currently marketed products based on less sustainable catalysts.
- Production of hydrogen from renewable energy.