A Taste of Our 2014 Harvest
Strong collaborations between ICIQ groups
Easily processable Single-Molecule Magnets
In the search for molecule-based materials for novel applications in the fields of materials sciences, P. Ballester and J. R. Galán-Mascarós teams have designed, synthesised and characterised a new family of complexes that exhibit single-molecule magnet (SMM) behaviour. Currently there is growing interest in such compounds as they could be used in the future for high-density information storage, which would allow us to increase the storage capacity of computer hard disks.
The main advantage of this new family of complexes is that they are very easy to process. That means, they are highly soluble in common organic solvents such as CH2Cl2 and can be sublimed under relatively mild conditions. This is a key point for further studies, since the next step is the deposition of monolayers of these complexes onto surfaces, for which they have to be dissolved and sublimated. It is therefore crucial when one wants to look for real applications.
These results have been published in Chemistry – A European Journal and highlighted in the ChemistryViews website.
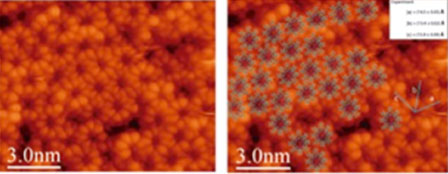
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) image of a layer of Dy(OETAP)2 molecules, as sublimed on gold. Image provided by David Écija and his team (IMDEA Nanoscience Institute, Madrid)
Ref:
Single-Molecule-Magnet Behavior in the Family of [Ln(OETAP)2] Double-Decker Complexes (Ln=Lanthanide, OETAP=Octa(ethyl)tetraazaporphyrin)N. Giménez-Agulló, C. Sáenz de Pipaón, L. Adriaenssens, M. Filibian, M. Martínez-Belmonte, E. C. Escudero-Adán, P. Carretta, P. BAllester, J. R. Galán-Mascarós
Chem. Eur. J., 2014, 20, 12817-12825
Enantioselective organo-photocatalysis with bismuth-based materials as photocatalysts
The development of chemical transformations that make use of sunlight as the energy source are currently subject of intense research, specially in the area of asymmetric catalysis, where photocatalytic methods have shown promising potential.
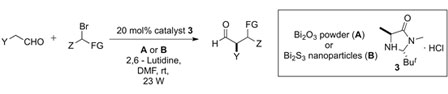
By working collaboratively, Miquel Pericàs and Emilio Palomares groups have used bismuth-based materials as photocatalysts in combination with a second-generation MacMillan imidazolidinone as the chiral catalyst to perform the α-alkylation of aldehydes with α-bromocarbonyl compounds with good yields and very high enantioselectivities. At first, the reaction was performed with simulated sunlight, but it also proved to proceed with high efficiency when the reaction vial was exposed to the morning sunlight on a clear day in Tarragona.
This process had been previously done using ruthenium complexes, but this is a scarce and expensive metal and its compounds are highly toxic and suspected carcinogens. In contrast, bismuth materials are abundant, rather inexpensive and non-toxic, which is a great advantage when performing these reactions.
Ref:
Light-Driven Organocatalysis Using Inexpensive, Nontoxic Bi2O3 as the Photocatalyst
P. Riente, A. Mata Adams, J. Albero, E. Palomares, M. A. Pericàs
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 9613-9616
Research on gold nanoparticles stands out
A paper published by Piet van Leeuwen, Atsushi Urakawa et al. in Journal of the American Chemical Society has been featured in Advances in Engineering for its contributing to excellence in engineering, scientific and industrial research.
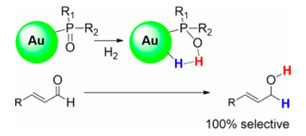
They have synthesised air-stable and homogeneous gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) stabilized by a secondary phosphine oxide (SPO). This is the first case that describes the use of SPOs as stabilizing ligands for AuNPs, but it is also the first that aims to investigate the role of these ligands in catalysis.
These types of AuNPs have been found to be very active catalysts for the highly chemoselective hydrogenation of substituted aldehydes. This work represents a clear demonstration of the ligand-metal cooperative effect, where the nature of the SPO ligand plays a crucial role and is directly related to the catalytic activity.
Ref:
Air-Stable Gold Nanoparticles Ligated by Secondary Phosphine Oxides for the Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Aldehydes: Crucial Role of the Ligand
I. Cano, A. M. Chapman, A. Urakawa, P. W. N. M. van Leeuwen
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 2520-2528